Please consider carefully any medical or health condition that would endanger yourself, or others on the trip, or diminish the enjoyment of an adventure vacation such as this. Factors of age, weight, lack of conditioning, heart or other disease can become exacerbated by the environment, remote distances from a hospital, and physical challenges of a rafting adventure. It is critical that you are in reasonable health and physical fitness at the time of departure so that our staff can focus their attention equally on all trip participants. If you are taking any medications, we should be made aware of these and what these medications are treating. If you have any questions or concerns please talk with us and we can help you consider your options.
PHYSICAL REQUIREMENTS:
- Fit into our Type 5 Life Jacket (maximum chest size is 52 inches and minimum weight is 50 pounds) required by the National Park Service.
- Each guest wears a lifejacket and they are very effective at keeping you above water, but if you are unable to swim, it can still be a threatening situation because the waters are turbulent. The lifejackets we supply are certified by the United States Coast Guard and are approved for use by our managing agencies (National Park Service, Bureau of Land Management & Utah State Parks & Recreation). They are classified as 'Type V Whitewater' jackets, and they come in two basic sizes 'Youth' and 'Adult Universal.'
- Youth lifejackets fit those weighing between 50 and 90 pounds (23-41kg). An Adult Universal Jacket is rated 'for persons weighing more than 90 pounds (41kg).' They are highly adjustable and fit a range of chest sizes from 30 - 52 inches (76-132 cm). Body shape can also affect the proper fit of the jacket. If you are unsure, call and speak with us. If unsure, we’ll mail you one of our jackets and you can try it on.
- Securely grip ropes provided for handholds while running the rapids.
- Gripping the ropes on the raft is the only way to ensure you stay on board. Factors such as where you sit in the raft in relation to where the waves crash can be a factor, but whitewater rafting can give an unpredictable ride.
- Falling off a boat into the river, or having your boat capsize is one of the inherent risks associated with whitewater rafting. If this happens, you will need the ability to self-rescue by swimming to the boat or to shore. If you end up on shore, you will need to traverse a rocky shoreline to rejoin the boat which cannot maneuver upstream.
- For those participants who have heart conditions or who are very overweight, falling into the river also presents the possibility of a 'cold-water immersion heart attack.' This is caused when the person swimming cannot calm his/her breathing within a reasonable amount of time (generally 60 seconds).
- Traverse and navigate uneven terrain over sand and rocks on hikes and in camp.
- Getting on and off the boats can be very challenging. We park the boats against a variety of terrain such as rocks, steep sandy beaches, and flat locations. Climbing onto a larger, motorized raft (J-Rig) requires a 2-3 foot high ascent. The boat is sometimes moving up and down and side to side when tied up in faster current. Boats may also be slippery and they have uneven surfaces. The front of the raft is turned up allowing it to climb waves. Because we have to park the rafts with the front against the shore, it makes a taller barrier to climb over when boarding or deboarding the raft.
- As we travel down river, we make occasional stops to lead 'side hikes' which can be either very short and relatively easy, or much longer, covering significant distances and elevation. We hike over uneven, rocky, and often steep surfaces. These beautiful hikes lead to sparkling streams, pristine pools, green fern glens and ancient American Indian ruins. Though all the hikes are not mandatory, when the rafts are tied up in swift current, all guests must get off the rafts and move up the shore a distance. Guests cannot be left on the rafts due to safety concerns. Reasonable mobility is important. If you have questions about your limitations, please call.
- In camp, you will need to have the same mobility over uneven terrain, and be able to carry your personal bags to your campsite while doing so. Also, keep in mind that paths from your campsite to the toilet facilities would not be classified as 'easy' to navigate at night.
- We camp and eat lunch on sandy beaches and on areas where the ground is mostly dirt and rocks. You must also be capable of safely walking across slippery, rocky, and sandy areas as you climb on and off the boat and walk along the beach to your personally selected campsite each night.
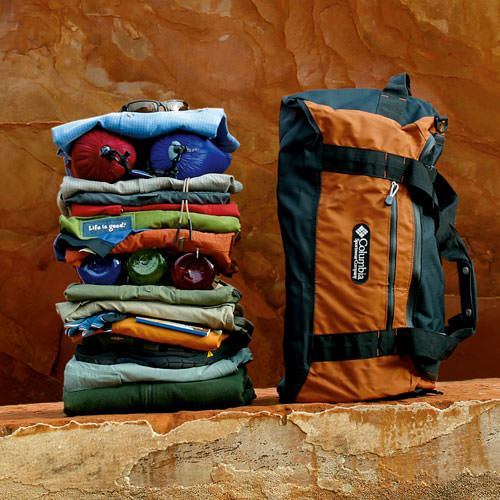
- Carry your own dry bag which will include your 20-pound duffle bag along with the sleeping bag and ground cover we provide.
- Guests are required to carry their own waterproof bags with personal gear and the additional 15 pounds of camping gear (cots & tents) to their individual campsite. This can be very difficult for some guests due to the uneven terrain, deep sand, and steep beaches. (Guests are also required to set up their own cots and tents, instruction will be provided.)
- A river trip is a participatory experience and requires each guest to be reasonably self-sufficient. Our guides will look after the safety and welfare of all the participants on the trip, but you are also responsible for your own safety! Our guides will provide you with the information and tools you need to participate; however, they already fill nearly every minute of their day performing their duties on behalf of the group. They will not be able to devote a lot of extra time to any one individual on the trip.
WEATHER:
- REMOTE LOCATIONS:
- Our trips are operated in the 'backcountry.' At any given time, you will be a minimum of several hours away from medical help. Our guides are all trained in wilderness first aid and some have even higher levels of emergency response training (e.g., EMT), however, sometimes injuries or the aggravation of pre-existing medical conditions are severe enough to require evacuation from the trip. We carry satellite phones but they are not 100 percent reliable in all locations. Most evacuations require transportation via helicopter which presents many challenges such as appropriate landing zones, inclement weather, darkness, or delays.